Planting the Apple Seed

How to plant an apple seed – Successfully planting an apple seed requires understanding the optimal conditions for germination and growth. While it’s a simple process, attention to detail significantly impacts the seedling’s chances of survival. This section will guide you through the specifics of planting your apple seed, covering depth, spacing, timing, and different planting methods.
Optimal Planting Depth and Spacing
Apple seeds are tiny, and planting depth is crucial. Too shallow, and they’ll dry out; too deep, and they won’t have the energy to reach the surface. Aim for a planting depth of about ¼ to ½ inch. This allows for sufficient soil cover to retain moisture and protect the seed while still being accessible to sunlight for germination.
Spacing is equally important, particularly if planting directly into the ground. Allow at least 6 inches between seeds to prevent overcrowding and competition for resources. This spacing ensures each seedling has enough room to develop a healthy root system and above-ground growth. Overcrowding leads to weak, spindly plants susceptible to disease.
Planting an apple seed requires careful stratification to break dormancy, followed by planting in well-draining soil. This process, while straightforward, differs significantly from the methods used for planting other vegetables; for instance, understanding the specific needs of warm-season crops like okra is crucial. For detailed instructions on cultivating this vegetable, please refer to this comprehensive guide on how to plant okra seeds , which will help you contrast the techniques with those employed when planting an apple seed, ultimately leading to successful germination in both cases.
Planting Schedule and Climate Considerations, How to plant an apple seed
The best time to plant apple seeds is in the fall, after the first frost but before the ground freezes solid. This mimics the natural process of seed dormancy, allowing the seeds to undergo stratification (a period of cold, moist conditions) before germination in the spring. The stratification period is crucial for breaking dormancy and improving germination rates.
However, the exact timing depends on your climate. For warmer climates, you might need to refrigerate the seeds for several weeks to simulate the winter conditions. In colder climates, direct sowing in the fall is usually sufficient. Always check your local frost dates to determine the optimal planting window.
Direct Sowing versus Container Planting
You can plant apple seeds directly into the ground or start them in containers. Direct sowing is simpler, but it exposes the seeds to more environmental challenges like pests, harsh weather, and competition from weeds. Container planting offers more control over the growing environment, allowing for better protection and easier management of watering and fertilization. Containers also make it easier to transplant seedlings once they are larger and more established.
However, container planting requires more effort in terms of monitoring moisture levels and preventing rootbound conditions. Choose the method that best suits your experience level and resources.
Comparison of Planting Methods
| Method | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Direct Sowing | Simple, less labor-intensive, mimics natural conditions | Higher risk of seed failure due to environmental factors, more competition from weeds |
| Container Planting | Greater control over environment, easier transplanting, higher seedling survival rate | More labor-intensive, requires monitoring moisture levels and preventing rootbound conditions, increased initial cost |
Caring for the Apple Seedling: How To Plant An Apple Seed
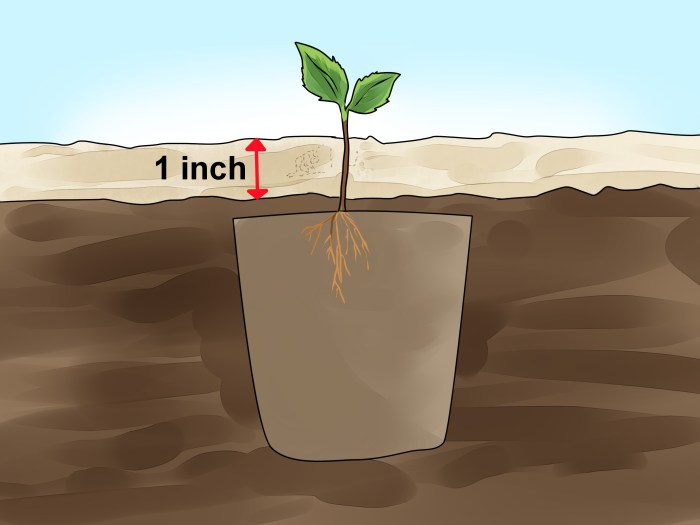
Once your apple seed has sprouted and developed its first few leaves, the journey to a mature apple tree is far from over. Careful nurturing during the seedling stage is crucial for its healthy development and future fruit production. This stage demands attention to several key environmental factors and consistent care.
Ideal Environmental Conditions for Apple Seedling Growth
Apple seedlings thrive in specific environmental conditions. Sunlight is essential for photosynthesis, providing the energy for growth. Aim for at least six hours of direct sunlight daily, ideally morning sun to avoid intense afternoon heat. A location with dappled shade during the hottest part of the day is beneficial, particularly in warmer climates. Temperature plays a significant role; apple seedlings prefer moderate temperatures, ideally between 65-75°F (18-24°C).
Fluctuations in temperature should be minimized as much as possible. Maintaining appropriate humidity levels is also important. Consistent moisture in the air, around 50-60% relative humidity, prevents the seedlings from drying out, especially during warmer months. Poor air circulation can lead to fungal diseases, so ensure good ventilation around your seedlings.
Watering Schedule for Apple Seedlings
Consistent watering is key, but overwatering can be detrimental. The watering schedule will depend on the seedling’s growth stage and the environmental conditions. During the initial stages, when the seedling is small and its root system is developing, keep the soil consistently moist but not soggy. Water thoroughly when the top inch of soil feels dry. As the seedling grows larger and its root system expands, you can gradually increase the watering frequency, but always ensure good drainage to prevent root rot.
During hot and dry periods, more frequent watering might be necessary. Observe the soil moisture regularly; if it feels dry to the touch, it’s time to water. In cooler months, reduce watering frequency as the seedling’s growth slows down.
Common Issues During Apple Seedling Development and Solutions
Several issues can hinder the growth of apple seedlings. Identifying these problems early and implementing appropriate solutions is critical for the seedling’s survival and healthy development. Common problems include damping-off, nutrient deficiencies, pest infestations, and diseases.
Troubleshooting Guide for Apple Seedlings
| Problem | Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Damping-off (seedling wilting and death) | Fungal infection due to overwatering or poor drainage | Improve drainage, reduce watering, apply a fungicide if necessary. |
| Yellowing leaves | Nutrient deficiency (e.g., nitrogen, iron) | Apply a balanced fertilizer specifically formulated for fruit trees. |
| Aphids or other pests | Insect infestation | Use insecticidal soap or neem oil to control the infestation. Handpick larger pests if possible. |
| Leaf spots or powdery mildew | Fungal diseases | Improve air circulation, remove affected leaves, and apply a fungicide. |
Transplanting the Apple Sapling

Successfully growing an apple tree from seed requires more than just nurturing a seedling; it involves carefully transplanting the sapling into the ground when it’s ready. This process is crucial for the tree’s long-term health and fruit production. Getting it right ensures the young tree establishes a strong root system and thrives.The ideal time to transplant your apple sapling is during the dormant season, typically late fall or early spring, before new growth begins.
Avoid transplanting during periods of extreme heat or cold, as this can stress the young tree and reduce its chances of survival. Choosing the right time minimizes transplant shock and allows the sapling to focus its energy on root development rather than leaf growth.
Soil Preparation for Transplanting
Preparing the soil properly is paramount for a successful transplant. Apple trees prefer well-drained, slightly acidic soil with a pH between 6.0 and 6.5. Amend heavy clay soils with organic matter like compost to improve drainage and aeration. Sandy soils benefit from the addition of organic matter to improve water retention. Before planting, dig a hole twice as wide and as deep as the root ball of your sapling.
This allows the roots to spread easily and encourages vigorous growth. Loosening the soil at the bottom of the hole further aids drainage. Consider adding a balanced, slow-release fertilizer to the backfill soil to provide essential nutrients for the young tree.
Proper Root Handling During Transplanting
Gentle handling of the roots is essential to minimize damage and ensure successful transplanting. Carefully remove the sapling from its container, avoiding any sudden jerks or pulls that could break delicate roots. If the roots are circling the container (a common occurrence in container-grown plants), gently loosen them with your fingers before planting. Damaged or broken roots should be pruned with clean, sharp pruning shears.
Avoid disturbing the root ball as much as possible, as this can damage the delicate root hairs responsible for nutrient and water uptake. Remember, a healthy root system is the foundation of a healthy tree.
Step-by-Step Transplanting Guide
- Dig the hole: As mentioned earlier, dig a hole twice as wide and as deep as the root ball. This ensures ample space for root expansion.
- Prepare the sapling: Gently remove the sapling from its container, carefully loosening any circling roots. Trim any damaged roots with clean shears.
- Position the sapling: Place the sapling in the hole, ensuring the root flare (where the trunk meets the roots) is at or slightly above ground level. Avoid planting it too deep.
- Backfill the hole: Gradually backfill the hole with the prepared soil, gently firming it around the roots to eliminate air pockets. Do not pack the soil too tightly.
- Water thoroughly: After planting, water deeply to settle the soil and help the roots establish contact with the surrounding soil. This initial watering is crucial for successful establishment.
- Mulch: Apply a layer of mulch (2-3 inches) around the base of the tree, keeping it a few inches away from the trunk. Mulch helps retain moisture, suppress weeds, and regulate soil temperature.
Clarifying Questions
Can I use seeds from any apple?
While you can, seeds from heirloom or organically grown apples generally have higher germination rates. Store-bought apples may have been treated with growth inhibitors.
How long does it take for an apple seed to germinate?
Germination can take several weeks to months, depending on the variety and stratification method. Patience is key!
What if my apple seedling doesn’t grow?
Check for proper watering, light, and temperature. Ensure the soil is well-draining and free of pests or diseases. Consider repotting if necessary.
When can I expect my apple tree to bear fruit?
This depends on the variety, but it can take several years, sometimes up to 5-10 years, before you see your first apples.
How do I protect my young apple tree from pests?
Regularly inspect your tree for pests and diseases. Use organic pest control methods if necessary, such as insecticidal soap or neem oil.
